lesson 1.4 - sensor-based interfaces
Sensor-based interfaces use sensors to detect environmental changes and trigger a pre-programmed action, enabling systems to automatically respond to their surroundings without direct user interaction.
Have you ever walked into a room and the light turned on by itself? Or played a game on a Nintendo Wii or Xbox Kinect where you had to physically move your body? If so, you've used a sensor-based interface! 🖐️ Today, we're going to explore these cool interfaces that let computers and devices see, hear, and feel the world around them. We'll find out how they work and then you'll get the chance to design your very own futuristic smart room!
Learning Outcomes
The Building Blocks (Factual Knowledge)
The Connections and Theories (Conceptual Knowledge)
The Skills and Methods (Procedural Knowledge)
Recall the definition of a sensor-based user interface.
Describe examples of devices that use sensor-based interfaces.
The Connections and Theories (Conceptual Knowledge)
Analyse how a sensor-based interface works by detecting input from the physical environment.
Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using sensor-based interfaces for different tasks and users.
The Skills and Methods (Procedural Knowledge)
Apply knowledge of sensors to design a smart environment that meets user needs.
Create a simple diagram and written description that explains how sensor-based systems can work together.
Digital Skill Focus: Analyse a scenario (a room in a home) and identify how different systems (sensors) can be integrated to solve a problem or improve an experience.
The Input-Process-Output Cycle
A sensor-based interface is a system that uses a sensor to detect a change in its environment and then performs an action. It's a simple but powerful three-step process:
1
Input (The Sensor)
A sensor is a piece of hardware that measures a physical input from its surroundings. Think of it like a digital version of our own senses.
[o t:"card" w:"640px"]
💡
Light sensors
Detect the level of ambient light.
|
Examples
Streetlights that automatically turn on when it gets dark, or a smartphone screen that adjusts its brightness based on the ambient light in the room.
[/o]
[o t:"card" w:"640px"]
🏃♂️
Motion sensors
(Infrared/PIR)
Detect movement.
|
Examples
Security lights that turn on when someone walks by, automatic doors at the supermarket, or video game consoles like the Nintendo Wii or Xbox Kinect. With these consoles, your body becomes the controller; the sensor tracks your movements and translates them into in-game actions.
[/o]
[o t:"card" w:"640px"]
🌡️
Temperature sensors
(Thermistors)
Detect changes in heat.
|
Examples
A central heating system that turns on when the room temperature drops below a certain point, or a smart oven that maintains a perfect cooking temperature.
[/o]
[o t:"card" w:"640px"]
👇
Touch sensors
These detect pressure or touch.
|
Examples
The touchscreen on your phone or tablet is a complex grid of touch sensors. A modern laptop's trackpad also uses a touch sensor to follow the movement of your finger.
[/o]
[o t:"card" w:"640px"]
👁️
Proximity sensors
Detect how close an object is without touching it.
|
Examples
A car's parking sensors that beep faster as you get closer to a wall, or a phone screen that turns off when you hold it up to your ear during a call.
[/o]
[o t:"card" w:"640px"]
🎤
Sound sensors
While used for speech interfaces, they also act as simple sensors.
|
Examples
Smart home devices that can detect the sound of a smoke alarm and send an alert to your phone, or security systems that react to the sound of breaking glass.
[/o]
[o t:"card" w:"640px"]
🫸
Pressure sensor
Reacts to pressure or force
|
Examples
An automatic gate which activates when a car passes over the sensor or an alarm sensor which is triggered when someone stands on it.
[/o]
2
Process (The 'Brain')
3
Output (The Actuator)
An electric motor (to open a door).
A light bulb (to turn on).
A heater (to turn on).
A speaker (to sound an alarm).
Examples All Around You
Once you know what you're looking for, you'll see sensor-based systems everywhere:
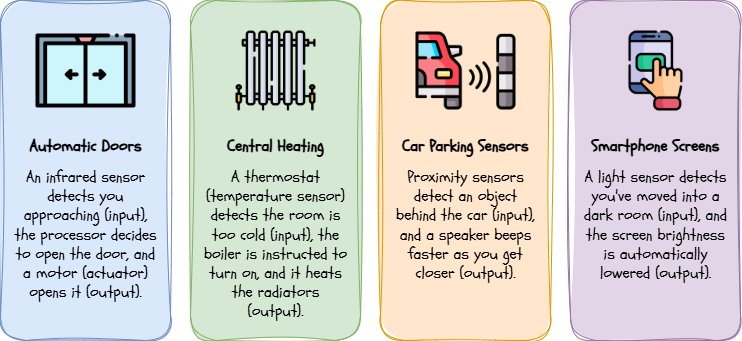
Sensor-based interfaces are a key part of the "Internet of Things" (IoT), where everyday objects are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other, creating a truly smart environment.
Task Design the Smart Room of the Future!
1
Get organised
1
Get into pairs or threes
2
Download and print out the worksheet "Smart Room Design", one for each member of your group.
2
In your group
1
Your team has been hired to design a smart room. First, decide on the type of room (e.g., Kitchen, Bedroom) and a target user (e.g., a teenager, an elderly person). Write this at the top of your worksheet.
2
Look at the 'Sensor Icons' list. Discuss where you could place at least four different sensors in your room to make life easier or more fun for your user.
3
Draw the icon for each sensor onto the 'Room Layout'.
4
For each sensor, draw a line to the object it controls (e.g., a light, a window, a speaker).
5
On the line, write a short note explaining the cause and effect. For example: "Light Sensor -> detects darkness -> turns on lamp".
Make sure each person in your group has a completed copy of the first part of the worksheet.
3
On your own
1
Choose one of the sensor systems you designed as a group.
2
On the sheet, write a detailed paragraph explaining it. You must include:
The specific type of sensor used.
What the trigger is (what does it detect in the environment?).
What action the device performs automatically in response.
Outcome: "I will have a completed 'Smart Room Design' diagram and a written paragraph in my workbook that clearly explains how one of my sensor-based systems works."

Application to the Component Sample PSA
Out of Lesson Learning
⭐ TASK
⭐⭐ TASK
⭐⭐⭐ TASK
Last modified: December 17th, 2025





















