lesson 3.1.3 the problem with numbers
Seriously, 73 is a number!

Ever had a computer misunderstand you? Today, we're tackling one of the most common (and frustrating!) bugs new programmers face. We'll learn why Python sometimes thinks the number
10Learning Outcomes
The Building Blocks (Factual Knowledge)
The Connections and Theories (Conceptual Knowledge)
The Skills and Methods (Procedural Outcomes)
Recall that
input()Describe the difference between an integer (a number) and a string (text).
Identify a
TypeErrorThe Connections and Theories (Conceptual Knowledge)
Explain why trying to add a string and an integer causes a
TypeErrorUnderstand that typecasting is the process of explicitly converting data from one type to another.
The Skills and Methods (Procedural Outcomes)
Apply the
int()Write a Python program that correctly takes numerical input and uses it in a mathematical calculation.
Digital Skill Focus: Apply keyboard shortcuts (e.g., Ctrl+C, Ctrl+V, Ctrl+S) to efficiently write and save code in a text editor.
Data Types?
Data comes in many shapes and forms. To make it easier for the computer to handle the data in the correct way, we group data into one of five main categories...

The five main data types.
Why is this important? Because the
input()The Problem with Numbers
In our last lesson, we learned how to get information from a user using the
input()Run the code by pressing the ▶️ button. Remember to press ENTER after you have entered your age.
🤔 Code Explainer
Line 1: Ask the user for their age and store it as a string in the variable
Line 2: Calculate their age in 5 years by taking their age and adding 5. Store it in the variable
Line 3: Print a polite message with their future age.
ageLine 2: Calculate their age in 5 years by taking their age and adding 5. Store it in the variable
future_ageLine 3: Print a polite message with their future age.
When we run this, the program crashes! It gives a
TypeErrorTypeError: cannot concatenate 'str' and 'int' objects on line 2This type of error is called a Runtime ErrorA error caused by an unexpected occurance during the operation of a program i.e. division by zero, file not found, incorrect data types etc. because it only occurs under certain circumstances after you run your script.
Why? Because the
input()"13"13Typecasting
To fix this, we need to convert the data type from a stringA sequence of characters delimited with quotation marks. to an integerA whole, positive or negative number.. This process is called typecastingI have no idea what this means - changing a variable's type. We can do this using the
int()Here's the corrected code, try running it again by pressing the ▶️ button.
🤔 Code Explainer
Line 1: Ask the user for their age and store it as a string in the variable
Line 3: Calculate their age in 5 years by converting age into an integer and adding 5. Store it in the variable
Line 5: Print a polite message with their future age.
ageLine 3: Calculate their age in 5 years by converting age into an integer and adding 5. Store it in the variable
future_ageLine 5: Print a polite message with their future age.
This now works perfectly! Understanding data types and knowing when to typecast is a super important skill for any Software Developer.
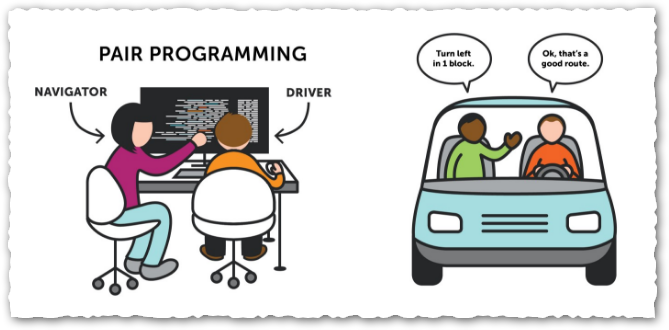
Are you a DRIVER or a NAVIGATOR?
Task The Broken Calculator and the Rectangle Challenge
Work in pairs. One person is the Driver (hands on the keyboard) and one is the Navigator (reads the instructions, thinks, and guides the Driver). Let's build a program that can add two numbers together. Follow the PRIMMI have no idea what this means steps carefully!
🤔 Code Explainer
Line 1: Print a friendly title
Line 2: Ask for the first number and store it in the variable num1
Line 3: Ask for the second number and store it in the variable num2
Line 4: Calculate the sum of the numbers (or does it?)
Line 5: Print the answer in a friendly format.
Line 2: Ask for the first number and store it in the variable num1
Line 3: Ask for the second number and store it in the variable num2
Line 4: Calculate the sum of the numbers (or does it?)
Line 5: Print the answer in a friendly format.

As a pair, look at the starter code in the widget.
If the driver enters
53Run
Now, the Driver runs the code.
Enter
53What was the result? Was your prediction correct?

Investigate
Discuss together: The program printed
538input()+Modify
The Navigator should guide the Driver. Modify the code to correctly convert both
num1num2answer = int(num1) + int(num2)
Run the program again. Does it now correctly calculate 5 + 3 = 8?
Make
Swap roles! The Driver is now the Navigator, and the Navigator is the Driver.
In the empty Python Widget below, create a "Rectangle Area Calculator".
Line 1 should ask the user for the
widthLine 2 should ask the user for the
heightLine 3 should then calculate the area (area = width * height). Remember to use
int()Line 4 should should print the answer in a clear sentence, like "The area of the rectangle is 30."

Outcome: We have worked as a pair to debug a program by identifying a
TypeErrorint()
int()Out of Lesson Learning
Last modified: November 21st, 2025





















