vacuum tubes
Learn the basic of vacuum tube operation.
The basic components of a vacuum tube are a glass tube (containing a vacuum), an emitter of electrons, called a cathode and a collector of electrons, called an anode.
A vacuum tube with two electrodes is called a diode (a di-ode) and acts as a rectifierI have no idea what this means because current (electron flow) can only pass from cathode to anode, not the other way around.
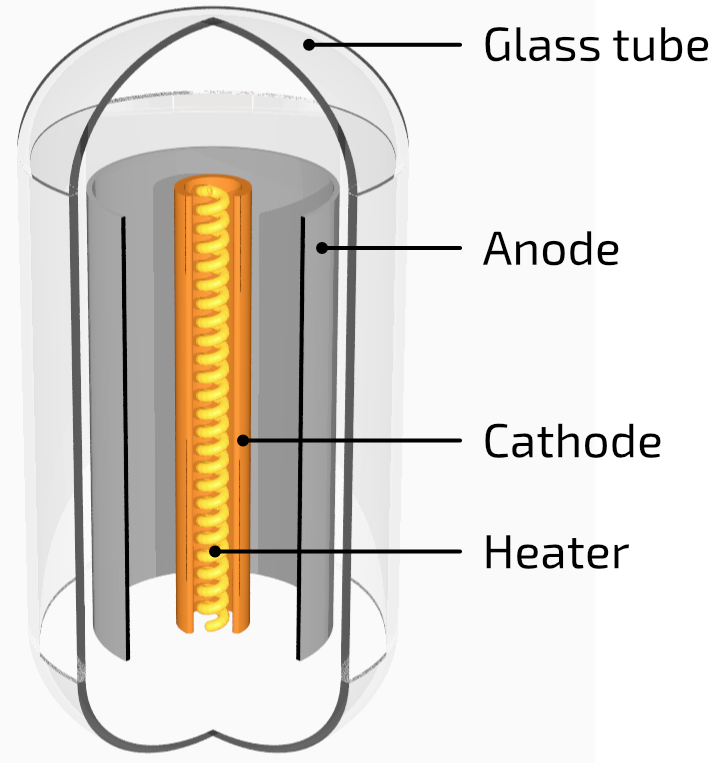
A simple diode vacuum tube
By adding a control grid between the anode and cathode produces a triode (tri-ode) where, varying the current between the grid and the cathode, the flow of electrons to the anode can be controlled.
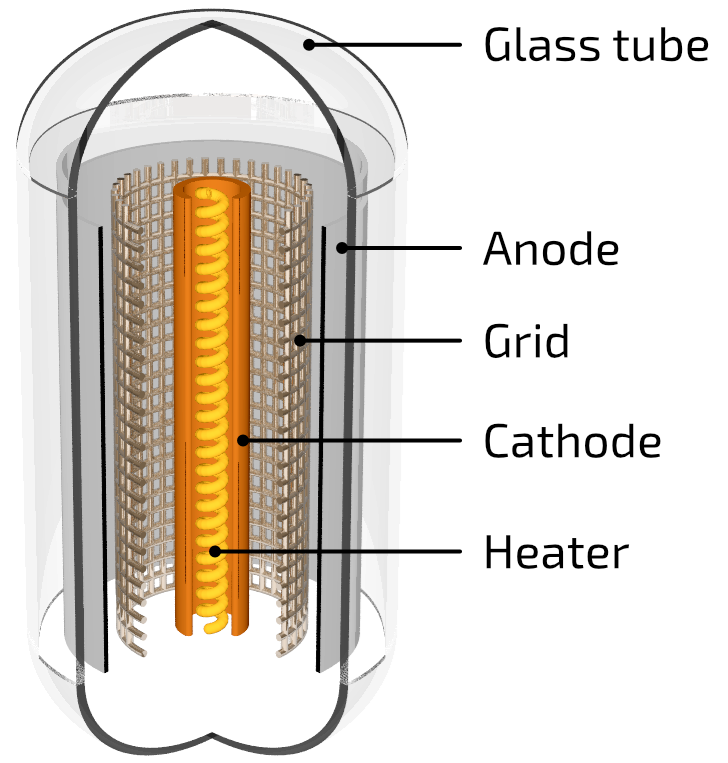
A simple triode vacuum tube
Applying a positive voltage to the grid accelerates electrons towards the anode (most of them miss the grid and pass right through) and increases the current flow between cathode and anode; applying a negative voltage to the grid repels the electrons and, if it is high enough, can stop the current flow all together.
So, by controlling the current on the grid voltage, you can control the current passing from cathode to anode - a primitive electronic switch. Also, if the grid voltage is quite small, but the main voltage is high, a small variation in the grid voltage can cause a large change in the main voltage and the vacuum tube can act as a crude amplifier.
Shortcuts
🌐
en.wikipedia.org
🌐
www.radiomuseum.org
🌐
www.apogeeweb.net
🌐
en.wikipedia.org
🌐
www.duncanamps.com
🌐
en.wikipedia.org
🌐
frank.pocnet.net
🌐
en.wikipedia.org
🌐
🌐
🌐
www.sm5cbw.se
🌐
www.r-type.org
🌐
www.tubecollectors.org
🌐
www.nutsvolts.com
Last modified: December 7th, 2021





















